USB drives or external hard drives may not be something you typically think of when you think of protecting your PC from malware, but Friendly Computers warns you that they are just as vulnerable to viruses and other malware as your main hard drive is. Read more below for information on how to secure your removable drives…
Removable drives are one of the most common infection vectors for malware today. Worms propagate via these vectors to proliferate their payload and ultimately, infect more users.
Users need to perform some countermeasures to secure their systems. One way of doing this is to protect removable drives against worms using the Autorun feature.
One popular way of protecting removable drives is by creating a folder or file and renaming it as AUTORUN.INF. It could enable the malware to automatically run on the system even without the users executing it. By creating this file beforehand, ideally, worms would not be able to run in this way.
However, this method is not perfect. Worms can delete the existing AUTORUN.INF file or folder, and then replace it with a malicious version. This would negate any protection placed by the user on the said file. However, by using file permissions to restrict changes, the AUTORUN.INF file can be protected more effectively.
Note: Make sure that your external drive is formatted using NTFS, as this procedure uses a specific feature of NTFS. If your removable drive is formatted using either FAT or FAT32, back up any data on the said drive first and reformat using NTFS. This may require Windows Vista or Windows 7.
- Create a new folder in the root directory of the removable disk and rename it as “AUTORUN.INF.”
- Create four more folders in the same location and named it as “recycle,” “recycler,” “recycled,” and “setup” respectively.
Note: The folders recycle, recycler, recycled and setup are optional but it is recommended for users to create these as malware often use these names/titles.
- Open a command prompt (cmd.exe) and go to the root directory of your removable drive.
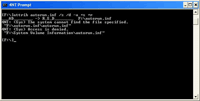
- Set the folder attributes using the following DOS command:
attrib autorun.inf /s /d –a +s +rFigure 1. Setting the folder attributes
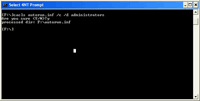
- Set the privilege level of the folder using the following DOS command:
cacls autorun.inf /c /d administratorsFigure 2. Setting the privilege level of the folder
- Select ‘Y’ and press enter when the message, “Are you sure (Y/N)?” is prompted.
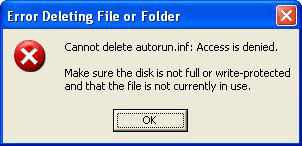
- To test it, try to delete, modify, rename, copy, or open the created folder. If you cannot perform any of these functions, then the procedure is successful.
Figure 3. When the user deletes the created folder, the system displays this message prompt.
In addition to the above procedure, users may also choose to use hardware means of protection. Certain removable drives have an external switch that prevents the device from being written to. This would prevent malware from making any modifications to the drive, including the AUTORUN.INF file. However, as this may prove to be somewhat inconvenient, it is still a good idea to use the procedure shown above.
Source: http://blog.trendmicro.com/how-to-maximize-the-malware-protection-of-your-removable-drives/